前言
如果你想了解命令行脚手架,这篇将带你入个门了解 commander 和 inquirer 库的使用。然后通过一个 Demo 示例来示范如何创作一个脚手架。
commander
首先需要知道 commander 这个 npm 库,它帮我们封装了 解析命令行 的能力。我们之后要做的脚手架都是基于 commander 的。
先了解几个简单的使用方式
显示帮助&版本信息
1 | const program = require('commander'); |
执行 node ./bin/fl-cli –help ,将看到如下效果:
1 | D:\project\frontend-learn-cli>node ./bin/fl-cli --help |
这个 program.parse 方法必须调用,不然命令行工具就不能“正常的工作了”。
输出信息中,能看到 Usage 条目,默认它向我们展示如何去使用这个命令,当然我们也可以更改它:
1 | program.usage('<command> [options]'); |
1 | Usage: fl <command> [options] |
如何约定命令 Command?
命名一个 create 命令,约定用于创建应用(类似 vue create)
1 | program |
通过 help 命令,能看到 Commands 条目中增加的新命令信息:
1 | D:\project\frontend-learn-cli>node ./bin/fl-cli --help |
执行 create 命令:
1 | D:\project\frontend-learn-cli>node ./bin/fl-cli create |
如何定义命令参数 Options?
我们需要额外增加参数,来让命令应对多种情况,比如可以设置 -f 使得创建的应用强制覆盖当前路径:
1 | program |
1 | D:\project\frontend-learn-cli>node ./bin/fl-cli create -f |
我们也能自定义参数值:
1 | .option('-f,--force <path>', '是否强制创建') |
1 | D:\project\frontend-learn-cli>node ./bin/fl-cli create --force /use/local |
需要注意,如果用户输入了 非预期 的参数将报错:
1 | D:\project\frontend-learn-cli>node ./bin/fl-cli create -abc |
我们可以添加 allowUnknownOption() 方法,防止 非预期 参数影响命令的执行:
1 | program |
1 | D:\project\frontend-learn-cli>node ./bin/fl-cli create -abc |
进阶技巧
如上,我们就能进行开发简单的命令行工具了。但离 人性化 的命令行工具还有点距离,下面提供几种技巧:
控制台输出语句的颜色
有个仓库叫 chalk ,让我们可以自定义 console.log 输出的颜色。这对于命令行有非常好的可视化效果。
我们对 –help 命令做个封装,在 help 信息末尾添加蓝色的帮助命令语句:
1 | const chalk = require('chalk'); |
1 | program.on('--help', () => { |
同时,遍历每个 Command 命令,也为其添加这一功能:
1 | program.commands.forEach((c) => c.on('--help', () => outputHelp(cliName))); |
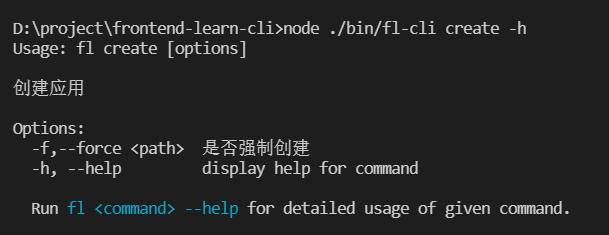
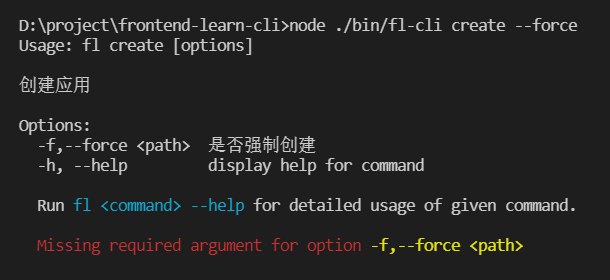
“命令/参数”错误的封装
由于命令错误,参数错误或者值漏填会导致命令行的出错,对于这类非预期的错误需要及时提示使用者,而不是只展示:error: option ‘-f,–force
参考 Vue 的错误处理 我们可以覆写 commander 的方法,结合 chalk 加强输出错误信息:
1 | var enhanceErrorMessages = (methodName, log) => { |
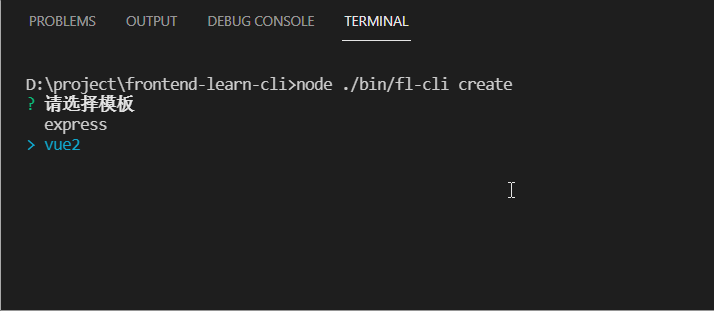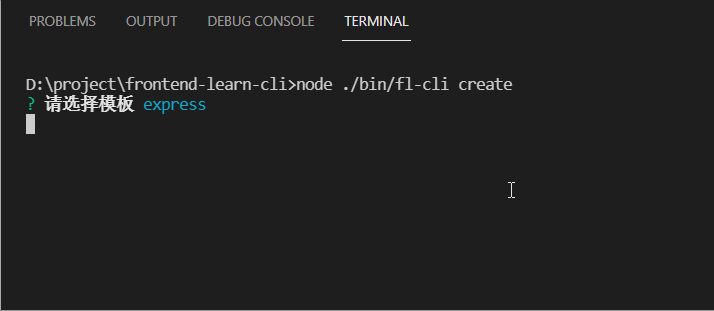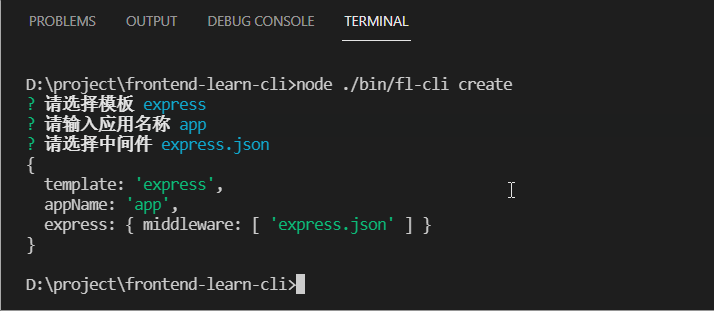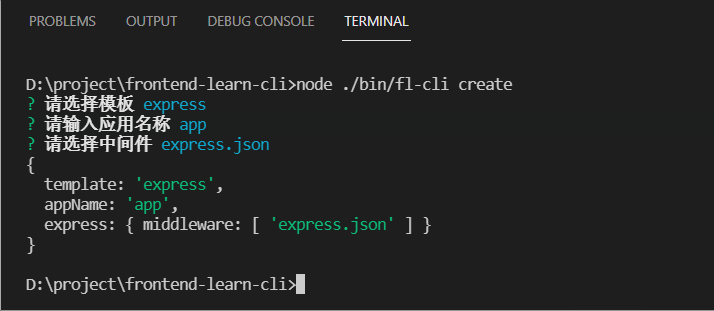
交互式命令行 inquirer
通过 command ,option 可以定义所有命令行需要的功能,但在与使用者交互会相当不友好(会面对大量的命令说明)。
相信用过 vue-cli 都知道:在创建项目时,我们可以跟随命令行的提示来选择对应需要的功能。
这种交互式的命令行可以通过 inquirer 来完成。
下面是采用了这种方式的效果图:
先定义一批 questions 交互问题:
1 | const defaultQuestions = [ |
然后在命令的 action 回调中调用 inquirer.prompt 方法:
1 | program |
当交互结束后,这个 answers 将是我们自定义的结果值:
1 | { |
Demo
再了解上面有关命令行的工具操作后,下面可以实际“造”一个脚手架工具了。
下面将提供一个创建 express 代码模板的脚手架。用于快速生成相关代码目录,而不用去技术栈网站去拷贝大量代码。(具体代码逻辑,在 npm 搜索 frontend-learn-cli 即可)
简单实现思路:
通过 commander ,实现对创建 create 指令的命令行解析
1 | program |
添加 inquirer 定义好相关可选问题
1 | inquirer.prompt(questions).then(async (answers) => { |
定义模板固定代码
根据自己对 express 的习惯,定义相关代码结构:
1 | template |
注意:上面的文件都已 ejs 作为后缀。具体原因是:模板变量会根据 answers 变量,动态注入自定义值。
ejs 文件模板会张这个样子:
1 | app.js.ejs |
为什么选择 ejs?
是抄 express-generate 这个库的,当然也可以根据自己喜好选择模板引擎。这种模板方式让我做这种脚手架变得很方便,只要把历史项目 demo 复制进来,改一通后缀即可。
通过 fs 读模板到指定路径
将模板内的文件通过 fs-extra 写到指令执行的当前路径下(文件具体操作这里就不详述了)
1 | inquirer.prompt(questions).then(async (answers) => { |
发布脚手架
在 package.json 文件中,约定 bin 属性,并指向我们实现 commander 的文件:
1 | "bin": { |
然后通过 npm publish 发布我们的脚手架包,最后使用者通过 npm i xxx -g 下载就能用了。
