graphQL
A query language for your API
GraphQL 用于作为 API 查询的一种语言,针对 API 服务提供全面、易懂的数据描述,使得客户端能够能容易,能好的获取数据。一个强大的developer tools
当然我们只看graphQL.js
快速上手
Basic Types 基础类型
- String
- Int
- Float
- Boolean
- ID
默认每个类型可以为空,可以定义!来特殊注明不能为空
1 | type Query{ |
如果 test 定义为 String,若没有数据将返回 null。
1 | {"data":{"hello":"Hello world!","test":null,"num":1}} |
定义 String!,若无数据,将报错:
1 | { "errors":[{ |
Passing Arguments 传递参数
1 | var schema = buildSchema(` |
使用 Express 构建 GraphQL 服务
1 | npm install express express-graphql graphql --save |
app.js
1 | var gql1 = require('./graph/test1.js'); |
graph/test1.js
1 | var { |
插件效果: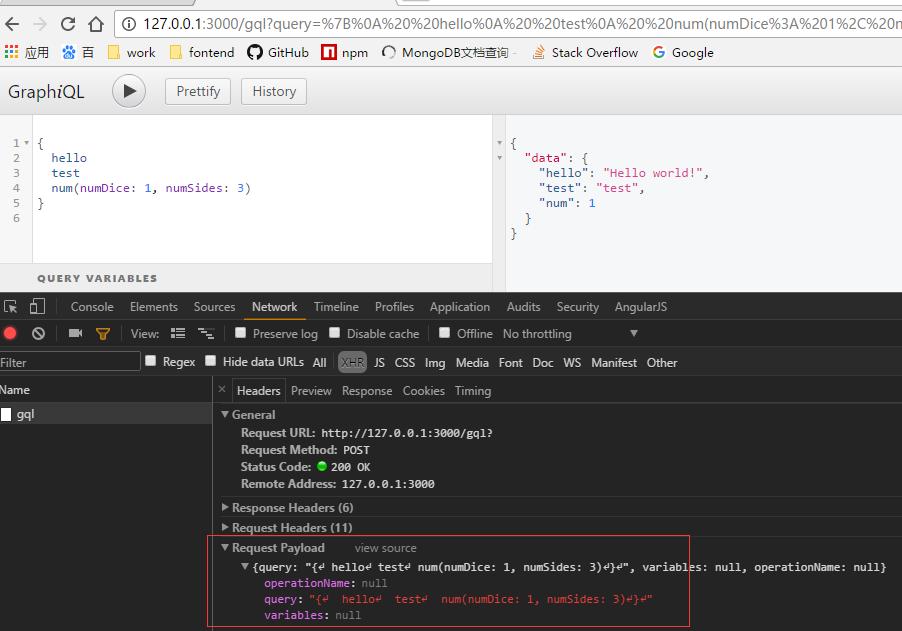
express-graphql会自动解析 req.query 的参数。当然还可以集成其他中间件 Middleware(Passport,express-jwt,express-session)来稳定、扩展这个微服务。
Mutations and Input Types 根据输入值改变行为
1 | let schema = buildSchema(` |
1 | // 定义Message对象 |
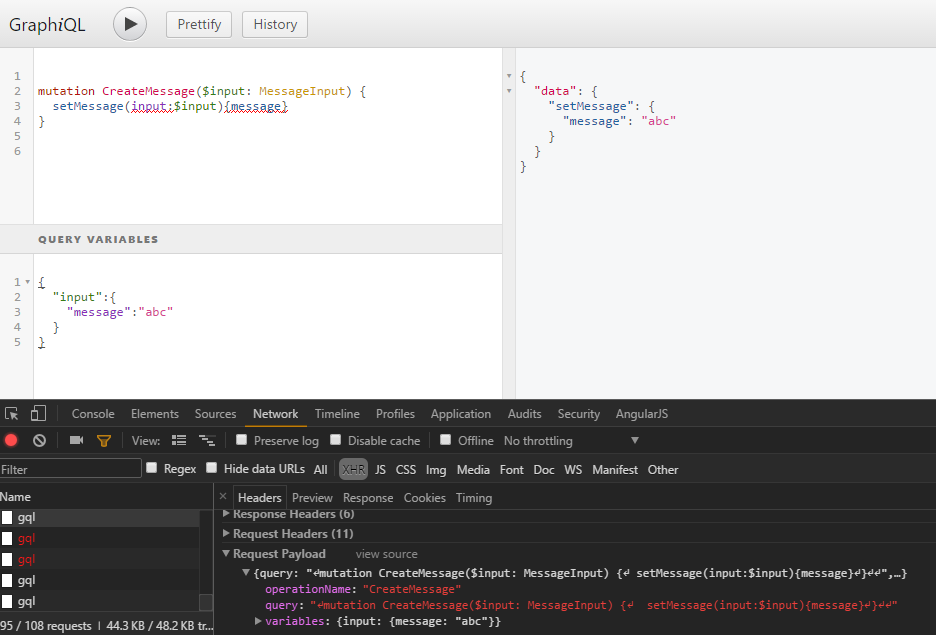
如果没使用 express-graph 方式:
1 | graphql(schema, |
Queries and Mutations 查询和转变
Fields 字段(像是定义一个对象)
在 query 定义 fields,来告诉 GraphQL 该查询什么数据与之对应。
每个 fields 有自己的 name,和字符串的 type(对象中属性)
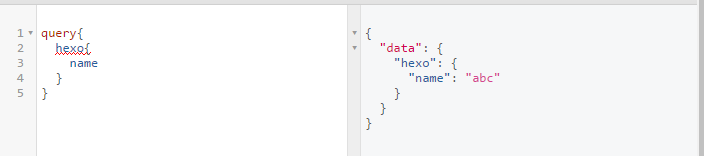
1 | let schema = buildSchema(` |
注意:
fields 中的属性可以按需定义,但是前提是 schema 要维护好。在这个前提下,query 可以任意增减属性,相当于数据过滤效果
1 | query{ |
Arguments 参数
在 query 定义参数列表,供 root 解析处理。
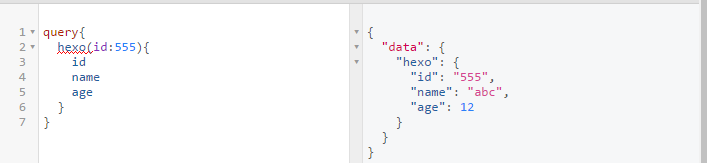
1 | let schema = buildSchema(` |
注意:
在 query 参数列表也要和 schema 定义一致;同时 root 中获取传入的参数需要通过解构来获取
1 | type Query{ |
Aliases 别名
query 通过类似泛型的说明(不知是否恰当),自定义返回数据的对象字段。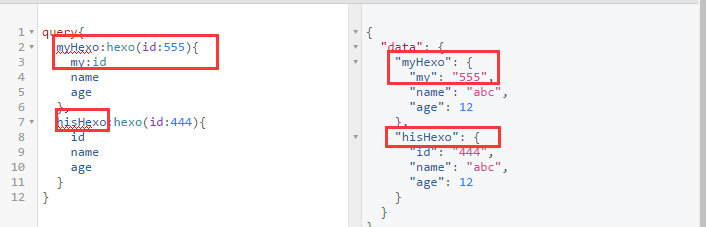
注意
对象,字段属性都是可以起别名的
Fragments 片段
类似上面那个需求,可能我们都很多复杂的字段,可以通过这种片段的方式简化 gql 代码。同时 fragments 又是依托于对象,理解 query 更为快速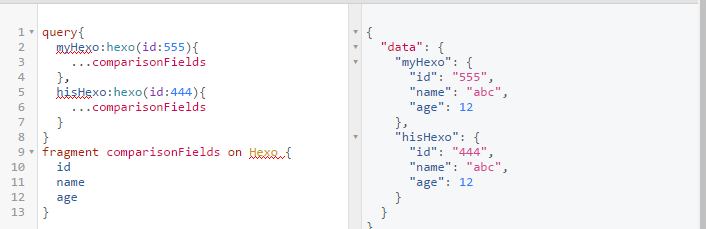
Inline Fragments
query 中,行内片段。多用于 interface 的数据
Operation name 操作说明
用于query, mutation, or subscription and describes,说明本次操作的意图。当然像 query,也可以省略 operation name(类似匿名查询)。
主要作用,更语义的说明 query 是干啥的,也在调试服务端时,分析 gql logger。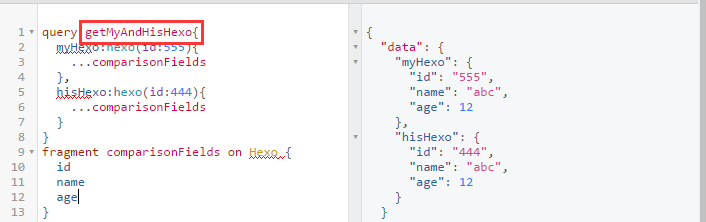
Variables 变量
上些例子,都是在 query 的 fields 上配置参数,并且参数是写死的。通常在实际应用上,我们需要动态可变的参数。
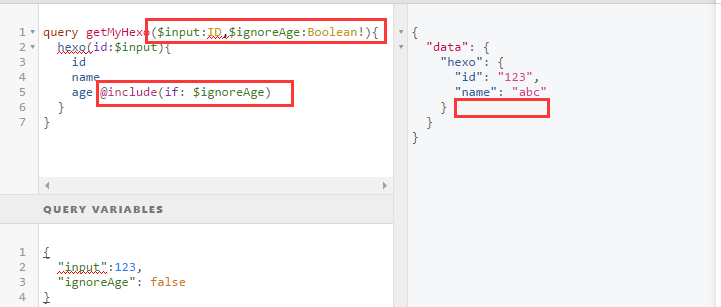
可以看下图中\$input: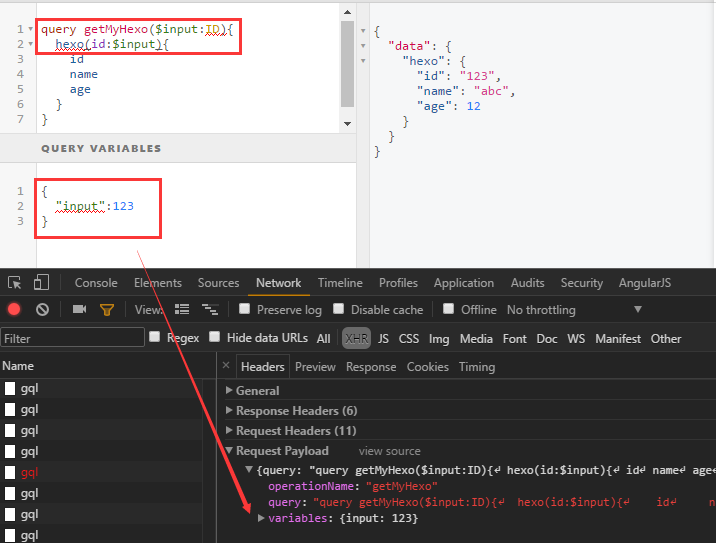
- 在 query 中,使用\$variableName类似占位符一样,定义静态值
- 在 query 上,声明\$variableName。
- 维护请求字段 variableName,传入数据
注意
- 声明参数,需要用\$前缀说明
- \$episode: Episode = JEDI 方式定义输入参数默认值
Directives 指令
可以制定 fields 中字段的显示,如果 field 中某个字段是对象,可以在指令后面继续和 field 定义字段方式一样,定义属性
1 | hexo(id:$input){ |
- @include(if: Boolean) Only include this field in the result if the argument is true
- @skip(if: Boolean) Skip this field if the argument is true.
 注意
注意
query 上的参数,需要指定!
Mutations 行为改变
GrapQL 是查询语句,但是避免不了某些查询会持久化数据或者更改,像 crud 里面的 create,update,delete 等情况。为区别 query,可以使用 mutations,就是体现这种约定。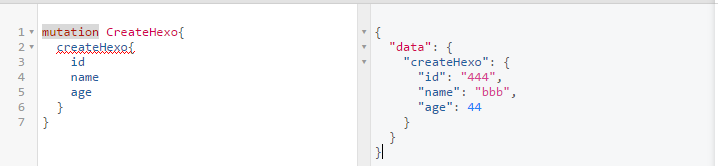
1 | let schema = buildSchema(` |
注意
搞清 mutation 和 query 区别,通常 mutation 也有自己的 mutation fields。mutation fields 是依次执行,而 query 的 fields 是并列
Meta fields
query 增加_typename,将返回 schema 的 type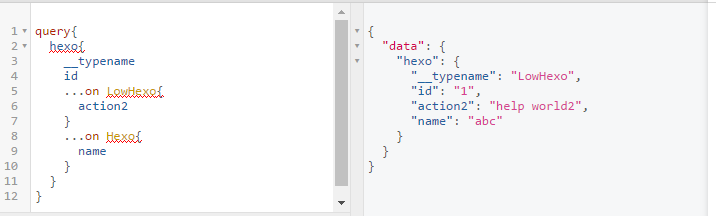
Schemas and Types
Type system
这是个简单的 query 语句,但能看到如下特点:
- 定义一个根对象,如果你隐去 query 和 operation name
- 设置一个 hexo,当做 fields
- 根据查询的数据对象,将包含 id、name fields
1 | query queryHexo{ |
Object types and fields
在 schems 中,定义 Hexo 这样一个 type,在 Query 中会使用到这个 type
1 | type Hexo{ |
- Hexo GraphQL Object Type
- id,name,age 作为 fields,在 Type 里
- 每个 field 将对应有 scalar types
Scalar types
fields 在解析时,会有对应的类型作为区分。
- Int: A signed 32‐bit integer.
- Float: A signed double-precision floating-point value.
- String: A UTF‐8 character sequence.
- Boolean: true or false.
- ID: The ID scalar type represents a unique identifier, often used to refetch an object or as the key for a cache. The ID type is serialized in the same way as a String; however, defining it as an ID signifies that it is not intended to be human‐readable.
Enumeration types
枚举类型,有个好处:对于已知的后台枚举数据,可以预先控制
1 | enum Action{ |
Lists and Non-Null
定义数据列表、非空类型
1 | type Hexo{ |
Interfaces
了解面向对象,基本知道抽象,实现之类的概念。
这里 GraphQL 也有这样的思想,如下:
可以定义一个 Animal,然后 Hexo,People 分别对 Animal 实现,并且扩展,有什么好处?
在不同查询结果中,可以维护不同的 type,来获取指定的对象数据。
1 | type Query{ |
